Stated Income Loans: Definition, Background, & Alternatives
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Stated income loans were home loans that didn’t require income verification or documentation.
- Stated income loans contributed to the 2008 financial crisis because people secured home loans they couldn’t afford, resulting in many borrowers defaulting.
- The original version of these loans no longer exists, but there are several alternatives to stated income loans available from lenders.
Stated income mortgage loans, also known as “no-doc” loans, allowed borrowers to secure financing by declaring their income without supporting documentation. While these loans provided flexibility for self-employed individuals and entrepreneurs, they played a controversial role in the 2008 financial crisis, leading to significant changes in mortgage lending practices.

Applying for a mortgage is a significant moment that means you’re ready to buy a house. Unfortunately, many home loans have strict lending criteria that prevent trustworthy borrowers from securing financing for a home or investment property. Over the years, the mortgage industry has evolved, creating more loan opportunities for borrowers of all types, including investors and the self-employed.
As you may know, it’s more challenging for entrepreneurs, investors, small business owners, and freelancers to secure a home loan because traditional mortgages come with stringent lending criteria. For instance, these individuals take deductions on their tax returns that reduce their taxable income, and they may have seasonal income that can affect their eligibility.
That said, many mortgage lenders understand that just because borrowers don’t meet traditional home loan criteria doesn’t mean they can’t pay off their loans, creating more loan options for individuals that don’t qualify for traditional loans.
For example, stated income loans were created to allow individuals to apply for a home loan without providing documentation. Instead, they simply stated their income, and their words were taken at face value. But what is a stated income loan, and do they still exist? Keep reading to learn more about these loans to help you find the best option for you and your family.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Stated income loans were home loans that didn’t require income verification or documentation.
- Stated income loans contributed to the 2008 financial crisis because people secured home loans they couldn’t afford, resulting in many borrowers defaulting.
- The original version of these loans no longer exists, but there are several alternatives to stated income loans available from lenders.
What Are Stated Income Loans?
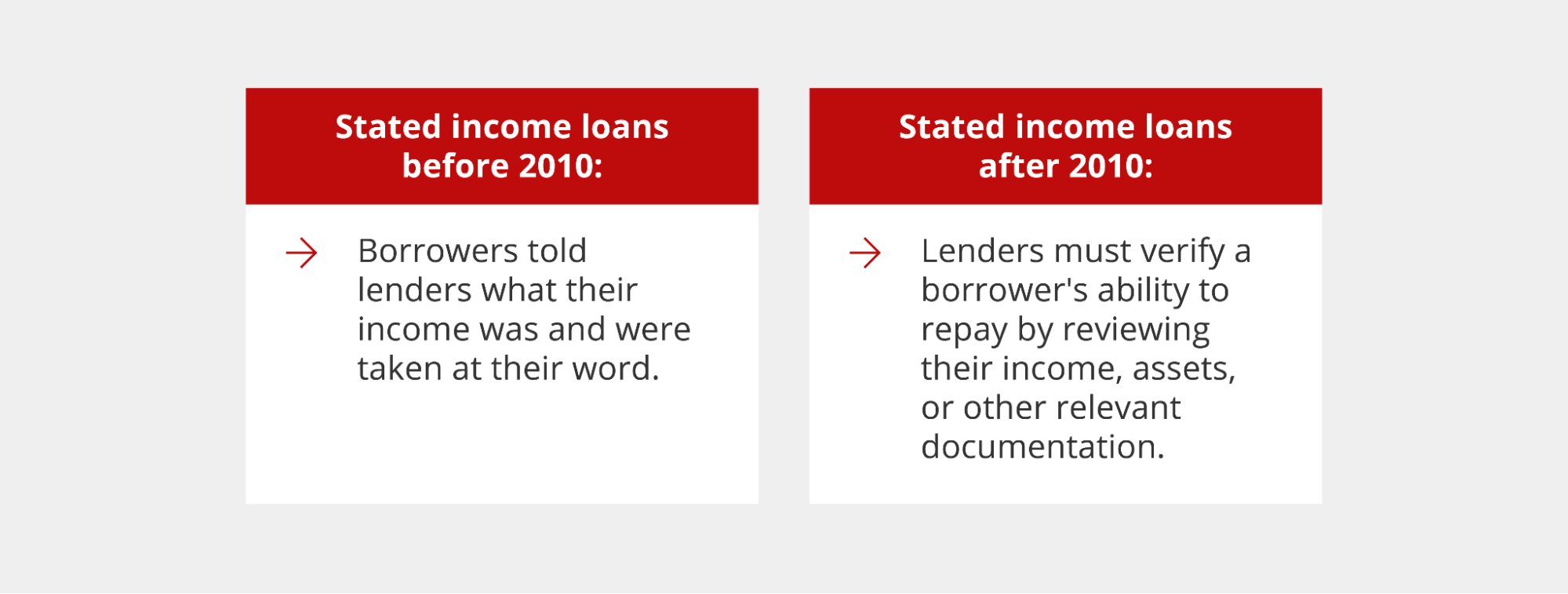
Stated income loans were originally a type of mortgage loan that allowed borrowers to qualify without income verification or documentation. Instead of providing tax returns or pay stubs, borrowers declare — or state — their income on the application, and lenders take their word for it instead of requiring verification through documentation like pay stubs or W2s.
Getting a loan with stated income is still an option today, but lenders must do their due diligence to ensure a borrower can afford to repay the loan. Applicants can no longer state their income on an application without providing some form of proof. Instead of using traditional methods, lenders verify your income using alternative methods, making it a good option for borrowers who may not qualify for traditional home loans, such as:

- Self-employed individuals and freelancers
- Entrepreneurs
- Retirees
- Small business owners
How Do Stated Income Loans Work?
Stated income mortgage loans work much like other mortgage loans. However, borrowers can no longer simply state their income. As of 2010, borrowers must provide proof of income through bank statements, tax returns, or other financial documents to prove their ability to repay the loan.
Stated income home loans improve the chances of borrowers getting approved for home loans because they don’t verify income with tax returns or pay stubs. Instead, they may use bank statements and look at the income deposited over a period of 12 or 24 months to determine how much a borrower actually earns. Then, the lender takes into account other factors like a borrower’s debts and credit score to evaluate their ability to repay the loan.
Stated Income Loans vs Traditional Mortgages
Stated income loans are Non-QM loans that require borrowers to state and prove their income, just like any other home loan. However, unlike traditional mortgages, the methods for verifying a borrower’s income are more flexible. For example, instead of relying on pay stubs, tax returns, and W2s, underwriters can use bank statements and other types of financial documents to verify someone’s income.
These loans can be beneficial for individuals who don’t have the necessary documentation to apply for a traditional loan. For example, self-employed individuals work for themselves and don’t have W2s or pay stubs. Additionally, small business owners take deductions on their tax returns, which effectively reduce their taxable income used as a determining factor for loan approval.
To help you understand, let’s say you’re a self-employed graphic designer who works for a variety of different clients. You earn $100,000 per year but deduct $40,000, making your taxable income only $60,000. Reducing your taxable income makes it so you owe less in taxes, helping you save money. However, traditional lenders verify your income by looking at your adjusted gross income after deductions, which is $60,000. So, ultimately, the tax return doesn’t accurately reflect a borrower’s ability to repay the loan. In reality, this borrower earns much more per year and may have a hefty savings account the lender doesn’t know about.
Depending on other factors, such as the borrower’s debt-to-income (DTI) ratio and credit score, they may not be eligible for a traditional home loan based on the information we have in front of us. However, they may still be eligible for a stated income loan because they can prove their income with bank statements rather than tax returns.
Of course, there are several other differences between today’s stated income loans and traditional mortgages, including:
- Interest rates: Non-QM loans, like stated income loans, typically have higher interest rates. While they’re less risky for the lender and borrower now than they used to be, they still carry more risk than conventional loans.
- Accessibility: These loans are not widely available and can be difficult to find as not all lenders or banks offer them.
- Down payment requirements: Since these loans are considered riskier for the lender, they may require you to put down a larger down payment. However, down payment requirements vary by lender. For example, Griffin Funding allows down payments as low as 10% for many Non-QM loan types.
History of Stated Income Loans
In the 2000s, mortgage lending requirements were much looser, allowing for easy access to no income verification mortgages. Stated income mortgage loans became popular because they allowed borrowers to qualify without income verification while allowing lenders to service more loans quickly to sell on the secondary mortgage market. Unfortunately, this led to unqualified borrowers receiving home loans only to default on them because they couldn’t actually afford them.
Stated income loans today are much different from the ones before the 2008 housing market crash. Back then, these loans were risky because they didn’t verify the borrower’s income at all. As a result, a borrower who wanted to buy a house with low income could list a higher income than they actually made, allowing them to get the loan but leaving them unable to pay their mortgage.
Following the recession, which was partially fueled by an overabundance of stated income loans, banks stopped offering them. Remember, the goal of a lender is to make money by servicing your loan. Therefore, they don’t want borrowers to go bankrupt or stop paying their loans.
However, stated income home loans resulted in many people around the nation being unable to repay their mortgages because lenders didn’t verify crucial information.
To remedy this issue, the government passed the Dodd-Frank Act in 2010, which set stricter criteria for these types of loans. The new loans are called qualified mortgage (QM) loans and consist of traditional mortgages that require the lender to verify the borrower’s ability to repay with W2s and 1099s if self-employed. Unfortunately, these new criteria made it more challenging for people who could repay their loans to become eligible for a loan.
Many borrowers don’t qualify under the Dodd-Frank guidelines because they can’t document their income as required. As a result, even if a borrower can repay the loan, they won’t qualify because they don’t have the necessary paperwork or because they reduce their taxable income with deductions on their tax returns.
Luckily, we have Non-QM loans to help borrowers of all types secure a home loan. Under the Dodd-Frank act, lenders must still verify a borrower’s ability to repay. Today’s stated income home loans are much different, but they reduce the possibility of borrowers defaulting on their loans while allowing for alternative underwriting methods to verify the ability to repay the loan.
Can You Still Get Stated Income Loans?
True stated income home loans that don’t verify a borrower’s ability to repay the loan no longer exist. However, stated income loans still exist under several different names. Unlike their predecessor, today’s stated income loans require lenders to determine a borrower’s ability to repay by verifying their income, DTI, and credit history.
Simply put, stated income loans in the traditional sense don’t exist. While borrowers must still state their income on a mortgage application, lenders must verify any information provided to ensure a borrower can afford the loan.
Alternatives to Stated Income Loans
Stated income loans have taken a new form, but they’re still available for borrowers with alternative income documentation. Today’s loans with stated income verification have more flexible lending requirements than conventional mortgages, enabling individuals without W2s or tax returns that accurately reflect their income to secure a home loan. A few alternatives to stated income loans that are popular today and offered as adjustable- or fixed-rate mortgages include:

Bank Statement Loans
Bank statement loans are a popular stated income loan alternative ideal for small business owners, self-employed individuals, and freelancers who take significant deductions on their tax returns and don’t have W2s. These loans typically require 12 to 24 months’ worth of bank statements instead of pay stubs to ensure borrowers have high enough monthly deposits.
With these types of mortgage loans, your lender will use bank statements to prove your ability to repay the loan. Additionally, you can use bank statement home equity loans if you need a second mortgage, even if your first mortgage isn’t a bank statement loan.
With these loans, you’ll still need to provide financial documentation of your income, but lenders will have a more accurate and complete picture of your financial situation to determine your eligibility. If you have personal and business bank accounts, you’ll have to provide statements for both to ensure you have enough money to cover the down payment and pay your monthly mortgage premium. In addition, lenders will want to know more about your particular situation. For instance, if you’re a small business owner, they’ll want to know about the number of your employees, the location of the business, and expenses.
Asset-Based Loans
Asset-based loans, also known as asset depletion mortgages, allow you to qualify for a home loan by using your assets as income to determine your ability to repay the loan. These loans are ideal for retirees, business owners, freelancers, and individuals with significant assets, even if they have a small fixed income.
With asset-based loans, you borrow against your assets, with the loan amount being determined by a percentage of their value. Lenders allow you to use 100% of your liquid assets and up to 70% of your retirement and investment accounts when applying for an asset-based loan.
These types of loans allow you to qualify for a home loan based on the assets you already have, such as your bank accounts and investment portfolios, so your current income isn’t a significant factor, although it can help. Asset-based mortgages are best suited for individuals with significant verifiable assets that don’t qualify for a traditional home loan based on their current financial situation. Assets can include things like:
- Checking and savings accounts
- Certificates of deposit (CDs)
- Money market accounts and mutual funds
- Stocks and bonds
DSCR No Income Mortgage
Debt service coverage ratio (DSCR) mortgage loans are designed for investors as a type of no income mortgage that allow individuals to purchase rental properties like single-family homes, condos, and apartments. With these loans, a lender determines if the income loan property (the rental property) can generate enough income to pay for the loan. To apply for these loans, borrowers must include estimates of projected rental income to be verified by the lender instead of using tax returns. With these loans, investors can avoid lengthy approval processes and strict lending criteria associated with conventional loans.
With these investment property loans, a lender determines if the income loan property (the rental property) can generate enough income to pay for the loan. To apply for these loans, borrowers must include estimates of projected rental income to be verified by the lender instead of using tax returns. With these loans, investors can avoid lengthy approval processes and strict lending criteria associated with conventional loans.
DSCR loans are a type of mortgage for investors only. You can’t use them to purchase a primary residence. Instead of traditional income verification, lenders calculate a borrower’s debt service coverage ratio to verify their ability to repay the loan.
The DSCR is calculated by dividing the property’s annual gross rental income by its annual debt (the mortgage and other costs like insurance), giving you a ratio. For example, if you have a gross rental income of $250,000 and an annual debt of $200,000, your DSCR is 1.25.
A ratio above 1.0 verifies that a borrower earns enough rental income to cover the mortgage. Lenders like to see a ratio of at least 1.25 to ensure the borrower can pay their mortgage and cover any expenses associated with the property, such as repairs or maintenance. However, some lenders allow DSCRs as low as 0.75, which typically comes with higher interest rates.
In any case, DSCR loans allow investors to qualify for mortgage loans based on the income loan property’s projected cash flow or rental income. These loans are ideal for both seasoned and novice investors who want to qualify for a loan based on the cash flow of the property rather than personal income, which may not accurately reflect how much they earn.
Tips for Securing Loans Similar to Stated Income Mortgages
There’s essentially no such thing as a stated income mortgage anymore because lenders are required to verify your income to determine your eligibility. However, there are many options available for borrowers who aren’t eligible for traditional loans. Non-QM loans make it easy for individuals who don’t qualify for traditional loans to secure a mortgage. However, you still must provide documentation to prove your ability to repay the loan. Here are a few tips to secure a mortgage similar to a stated income loan:

Prove income stability
To qualify for any type of home loan, you need to prove income stability. This doesn’t mean you can’t get a loan if you have seasonal income, but it does mean that you must earn enough or have enough in assets to cover your monthly mortgage payments. To prove income stability, you’ll need to share financial documents with your mortgage lender.
Lenders typically request the following documents to verify income:
- Personal and business bank statements from the past 12-24 months
- Tax returns and business profit & loss statements
- Documentation of any recurring payments or retainer agreements
- Proof of consistent client relationships or contracts
- Business licenses and incorporation documents
- Recent invoices to payment receipts from clients
Even if your income changes drastically from month to month, your lender will be able to determine if you earn enough annually to qualify for the loan. It’s important to note that even if you’re providing 12 months of bank statements, your lender may still require you to prove that you’ve been self-employed for a period of at least two years. If you haven’t been, some lenders may be more lenient if you’ve stayed within the same industry performing the same job function.
In addition to proving income security, you’ll have to provide information about your employment status or business.
For example, if you’re self-employed, you’ll explain the industry you’re in and what type of work you do. In this case, a freelance graphic designer will share information about the types of clients they work with, how they’re paid and whether they’re on retainer, and prove that their source of income is reliable. Meanwhile, a small business owner may provide documentation about the number of customers and employees they have.
Review your debt-to-income ratio
Your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio reflects the percentage of your income that’s used to pay off your current debt. It’s calculated by dividing your monthly debt by your monthly gross income and multiplying that figure by 100 to give you a percentage.
For example, if your monthly debt equals $2,000 and your monthly income is $6,000, you have a DTI ratio of 33%. Most traditional lenders like to see a DTI of 43%. However, every lender is different. For example, Griffin Funding allows for DTIs as high as 55%. However, a higher DTI can impact your eligibility and loan amount.
Monitor your credit score
In addition to your income and DTI, your credit score is an important determining factor and can help lenders determine how you handle debt. A high credit score tells lenders that you’re a borrower who pays back their debts on time, while a low credit score indicates that you have difficulty managing your debts. Your credit score reflects your creditworthiness, indicating to lenders the likelihood that you’ll repay your loan.
The minimum credit score to qualify for a home loan varies by lender, but you should aim for good or better. The higher your credit score, the better terms you can get. For example, a higher credit score can reduce your interest rate, saving you money over the life of the loan.
In addition to this number, lenders will review your credit history and all the components that make up your score. Key factors they evaluate include:
- Number and types of credit accounts (credit cards, personal loans, student loans, etc.)
- Total amounts owed across all accounts
- Length of credit history and age of accounts
- Payment history and on-time payment record
- Recent credit inquiries and new account openings
- Credit utilization ratio (amount of available credit currently in use)
This information can help lenders understand your borrowing and spending habits while ensuring you have a history of making on-time payments.
Separate business accounts
When applying for a Non-QM loan with bank statements, you must provide your personal and business bank statements. It usually makes it easier for lenders to sift through your information by separating business from personal expenses to ensure you can repay your debts. When reviewing bank statements, lenders will ensure that you earn enough every month to cover your mortgage payments, have regular monthly deposits to ensure income stability, and have enough money to cover the down payment and closing costs.
Explore Stated Income Loan Alternatives

True stated income loans no longer exist, but several alternatives exist for individuals who don’t qualify for a traditional home loan. Today, many lenders still call them stated income loans. However, they’re actually alternatives to the original stated income loan because lenders must verify a borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
These loans are a good option for individuals who take substantial deductions on their tax returns or don’t qualify for traditional loans because of strict lending criteria. Wondering if Non-QM loans are right for you? Contact Griffin Funding today or download the Griffin Gold app to learn more about our loan programs and find the best option based on your financial situation.
Find the best loan for you. Reach out today!
Get StartedFrequently Asked Questions
Are stated income loans illegal? 
Do stated income business loans still exist? 
Are stated income loans coming back? 
- Bank statement loans: This loan type uses 12-24 months of personal bank statements to qualify a borrower for their loan. In the case that a borrower has a business account as well, they’ll need to provide bank statements for that account, too.
- Asset-based loans: Also known as asset depletion mortgages, these loans look to the value of your assets as your income. Asset-based loans are a good option for retirees or individuals with significant assets, but small, fixed income.
- DSCR no-income mortgages: Debt service coverage ratio (DSCR) mortgage loans are intended for borrowers purchasing properties that they plan to use as a source of income, like an apartment or rental property. Borrowers are qualified based on the projected future income generated by their property.
How do I apply for an alternative mortgage program? 
- Research lenders who specialize in non-QM loans or alternative documentation programs.
- Gather relevant documentation such as bank statements, asset statements, or business records.
- Contact multiple lenders to compare rates and requirements.
- Submit an application with your chosen lender, who will guide you through their specific documentation requirements and approval process.
What are the best conventional loan types for self-employed borrowers? 
Self-employed people with significant assets but low income may also be interested in an asset-based loan. These loans are qualified based on the value of the borrower’s assets, rather than their income.
Self-employed borrowers have many mortgage options depending on if they can qualify using their tax returns or not.
Recent Posts
Current Mortgage Rates
What Affects Mortgage Rates? Mortgage rates fluctuate constantly based on a variety of economic variables and ...
Mortgage Refinance Limits
Your Refinancing Options Most owners have several refinancing pathways depending on their financial goals and ...
Pros and Cons of FHA Loans
What Is an FHA Loan? An FHA loan is a mortgage insured by the Federal Housing Administration, a division of th...



