If You Have a High DTI, What Can Happen?
When you apply for a mortgage loan, you must meet the lender’s criteria for approval. Your income, job history, debt, and other financial factors will play a role in eligibility, loan approval, and loan amount.
You’re not disqualified from securing a home loan if you have debt. Instead, lenders compare your debt to your income to determine if you have enough money left every month to pay your mortgage premium. Lenders calculate your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio to determine your ability to repay the loan based on various factors like income and debt obligations.
If you have a high DTI, you may still be eligible for a loan, but it’ll likely be harder to qualify for one. Instead, lenders can deny your application and ask that you reapply once you’ve reduced your debt or increased your income to meet their lending requirements.
So what happens if you have a high DTI? Keep reading to learn more about the debt-to-income ratio and what it means for you.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Lenders use several factors to determine your eligibility for a loan, including your debt-to-income ratio.
- Having a high DTI ratio can make you ineligible for a loan.
- Even if you qualify for a loan with a high DTI, your loan may come with less favorable terms like higher interest rates and fees.
Recap: What is a Debt-to-Income ratio?
Debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a percentage of a borrower’s gross monthly income used to pay their debts and other bills.
Lenders use this number to determine whether or not you can afford to repay your mortgage by demonstrating how risky of a borrower you are. Low DTI ratios mean that a borrower has a balance of income and debt that allows them to afford a mortgage payment.
For example, if your DTI is 20%, it tells lenders that only 20% of your income goes toward paying debt, which means you have 80% left over.
If you have a high DTI, what can happen? Ultimately, a high DTI tells lenders that you might not have enough income left over to pay your mortgage payment, signaling that you’re a higher-risk borrower if they choose to approve your mortgage application.

Conversely, borrowers with low DTIs can manage their debts and likely won’t take on more debt before applying for a loan.
Lenders must ensure that you can effectively repay your loan. A high DTI tells them you might be overextending yourself financially and have too many debts to pay your monthly mortgage premiums.
If you need to learn how to figure out your debt-to-income ratio, follow this formula:
DTI ratio= (Gross monthly debtGross monthly income ) x 100
What Is Considered a High DTI?
Most lenders and financial institutions like to see a DTI of 43% or lower. In this case, you spend less than half of your income on monthly debts. That said, some lenders require an even lower DTI.
However, if you can keep your DTI ratio below 43%, you are likely to be in a good position to get approved for a home loan. The range for what’s considered a high DTI varies. For example, a DTI of 43-49% indicates that you’re close to spending too much of your income on debt obligations for lenders to approve you for a loan.
Meanwhile, a debt-to-income ratio of 50% or more indicates that you’re spending at least half of your income on debts. As a result, lenders typically view these borrowers as high-risk because it shows that they struggle to pay their bills.
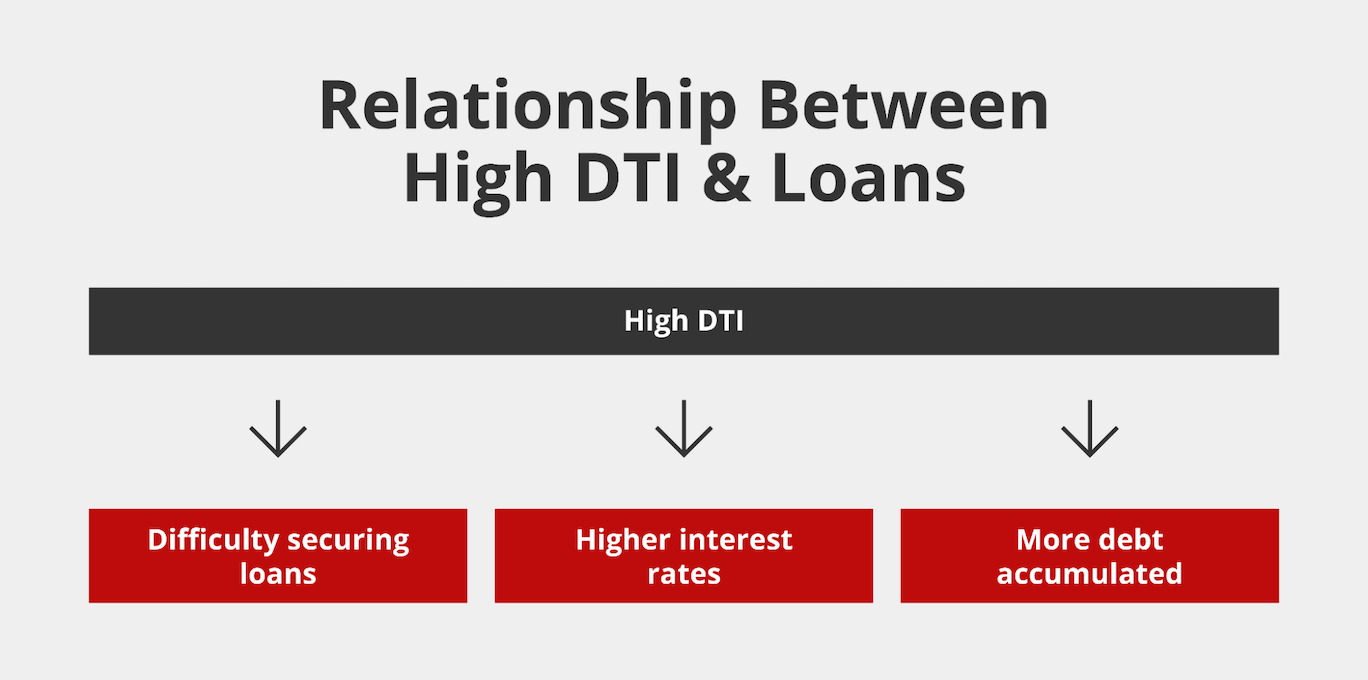
Effects of a High DTI
In general, mortgage lenders and other financial institutions prefer a maximum DTI of 43%. However, lenders prefer to see a debt-to-income ratio below that to demonstrate that your current debts won’t affect your ability to repay your mortgage loan.
In general, a high DTI insinuates that you struggle to pay your debts on time, and your budget is less flexible for more debt.
In addition, you may not qualify for a variety of loans, including personal and home loans. Even if you do get approved for a loan, your high debt-to-income ratio can yield you less favorable terms and higher interest rates because you’re seen as a riskier borrower to lenders.
Loan Qualification
The most significant impact of a high DTI is not being able to qualify for loans. As we’ve mentioned, a high DTI tells lenders that you may already be stretched too thin to take on more debt. Since mortgage loans are typically more expensive than other types of debt, lenders can deny your application if your DTI ratio is higher than 43%.
Of course, other factors, such as your assets and savings, can play a role in loan qualification, so having a high DTI doesn’t automatically make you ineligible. But it can make it more challenging to secure a home loan.
Interest Rates
Even if you can secure a home loan with a high DTI ratio, lenders need to mitigate the risk of providing you with financing. Since your high DTI ratio indicates that you might be overextending yourself already, your lender might safeguard themselves against your inability to repay your loan by giving you higher interest rates.
Typically, the lower your debt-to-income ratio and the higher your credit score, the more favorable terms you can get.
Higher interest rates mean paying more over the life of the loan. Even if you’re approved for a loan, it’s crucial to determine if you want to pay much more due to high interest rates that can impact your finances many years into the future.
What DTI Is Required to Qualify for a Home Loan?
Most lenders and mortgages require a DTI of 43% or lower. Ultimately, you should aim for no more than 43% of your gross monthly income going toward debts, including a new mortgage loan. Therefore, if you apply for a loan with a DTI already at 43%, you’re less likely to get approval for a conventional loan with strict lending requirements.
Luckily, there are several loan programs available for borrowers with bad credit. But again, the worse your credit and the higher your DTI ratio, the higher your interest rates will usually be.
Your DTI is Too High. Now what?
If you have a high DTI, there are several things you can do to take action and start reducing it before applying for a loan. A few ways to improve your chances of getting approved for a home loan include the following:
Find Forgiving Loans
Some loans have more flexible lending criteria that allow you to qualify for a home loan with a high DTI ratio. For example, FHA loans for first-time home buyers allow DTIs as high as 50% in some cases, even with less-than-perfect credit.
VA loans are the most flexible in terms of lending criteria because they allow qualifying veterans, active duty service members, and surviving spouses to put down as little as zero percent on the loan.
Every loan program and lender has different qualifying criteria, so it’s crucial to understand your options to find the best loan programs based on your financial situation.
Refinance Your Debt
You may be able to reduce your DTI ratio by refinancing or restructuring your existing debt. For example, you may be able to refinance student loans, credit cards, personal loans, and existing mortgages for a lower interest rate or longer repayment terms.
Debt consolidation is also an option. If you have multiple credit cards, you can take out a new loan to pay for the old ones and put at least some of your loans into a single monthly payment instead of trying to keep track of them.

Consolidating your debt won’t automatically reduce your monthly debt obligations, but your new monthly payment can be less than what you were paying before.
Cash Out
If you have an existing mortgage, using a cash-out refinance can help you lower your DTI by leveraging your home’s equity to pay off your debts to lower your DTI.
A cash-out refinance allows you to take one lump sum and use it however you like. However, if you want to lower your DTI, you can use that money to lower your monthly debt obligations and even pay off significant debt.
Get a Cosigner
If you don’t qualify for a loan based on your high DTI, lenders will look more favorably on you if you get a cosigner.
A cosigner is someone who is willing to take responsibility for the loan if you fail to repay it, so they’re typically family members. When you have a cosigner, your lender will use each party’s DTI to determine your eligibility.
How Do You Lower Your DTI?
Lowering your DTI is important if you want to ensure your eligibility for a loan and get more favorable terms whenever you take out a loan. A few ways you can lower your DTI include the following:
Pay Off Debts
If you have existing debt, paying it off can drastically reduce your DTI. For example, let’s say you earn $5,000 monthly and pay $2,000 toward debt every month. This gives you a DTI of 40%. While this DTI can still help you qualify for a loan, lenders like to see DTIs of 36%, so you can try to lower it before applying for a loan by paying off your debts.
Let’s say your income stays the same, and you paid off enough debt to only have $1,500 in debt obligations every month. Your new DTI is 30%. Paying off your debt is the easiest and most efficient way to lower your DTI.
Increase Your Income
Increasing your income is another way to reduce your DTI ratio because even though your debt stays the same, a lower percentage of your income will go toward paying it off. Luckily, there are several ways to increase your income, such as applying for a promotion at work or working side gigs to supplement your salary.
Report any new positions or jobs to your lender, so they have all the necessary financial documentation.
Extend the Duration of Loans
If you can’t lower your loan amounts or increase your income, you can try to extend the duration of your loans to reduce how much they cost you every month.
You may be able to get new loan terms by discussing your options with your lender. However, it’s worth noting that you may have to pay higher interest rates.
Find Loan Options for Borrowers with High DTI
Having a high DTI won’t make you ineligible for a loan automatically, but it can affect your eligibility when compared to your income, credit score, and other factors. In addition, having a high DTI is a red flag to lenders that tells them you’re a riskier borrower, and they may mitigate their risk by giving you higher interest rates and other fees.
Griffin Funding offers loans with more flexible requirements to help borrowers of all types secure a home loan. Contact us today at 855-698-1098 or apply online to find out if you qualify for any of our loan programs.
Interested in learning more?
Get StartedFrequently Asked Questions
Is DTI more important than your credit score? 
Since it compares current debts to income, it can tell lenders how much income a borrower has left over to pay their mortgage.
How do you calculate DTI? 
DTI ratio= (Gross monthly debt / Gross monthly income ) x 100
If you have a DTI higher than 43%, you can use some tips outlined in this article to help you reduce your DTI before applying for a loan.
What DTI is needed for a VA loan? 
The ideal ratio for a VA loan is similar to other types of loans. However, the VA doesn’t set these limits. Instead, private lenders determine their DTI limits to qualify. Some lenders allow DTI ratios as high as 55% for VA loans, while others stick to the 43% limit.
Recent Posts
Bonus Depreciation for Real Estate: What It Is & How It Works
Understanding the concept of bonus depreciation and its practical application can help you capitalize on this ...
No Doc Business Loans: What You Need to Know
While “no doc” is short for “no documentation,” there are actually no true no doc loans. Instead, they...
BRRRR Method: Buy, Rehab, Rent, Refinance, & Repeat
Read on to learn more about BRRRR loans and explore how this approach can open doors to lucrative opportunitie...

