How Will Tariffs Affect the Housing Market?
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Tariffs on building materials directly increase construction costs, which builders pass on to home buyers through higher prices.
- The housing market and tariffs connection is strongest for new construction, but existing home prices also rise due to reduced inventory.
- Regional markets experience different impacts based on local building practices and material sourcing.
- Home buyers should consider timing purchases carefully and work with experienced lenders who understand market volatility.


 Outstanding Client Experience
Outstanding Client Experience Specialized Lending Solutions
Specialized Lending Solutions Direct-to-Consumer Advantage
Direct-to-Consumer Advantage We're Advisors, NOT Salespeople
We're Advisors, NOT Salespeople Effortless Digital Mortgage Platform
Effortless Digital Mortgage PlatformTrade policies might seem disconnected from your home buying plans, but tariffs can significantly impact housing costs and availability. When governments impose tariffs on imported materials, the effects ripple throughout the construction industry and eventually reach your mortgage payment. Understanding these connections helps you make better decisions whether you’re buying, selling, or refinancing.
So, how do tariffs affect the housing market? Keep reading to find out.
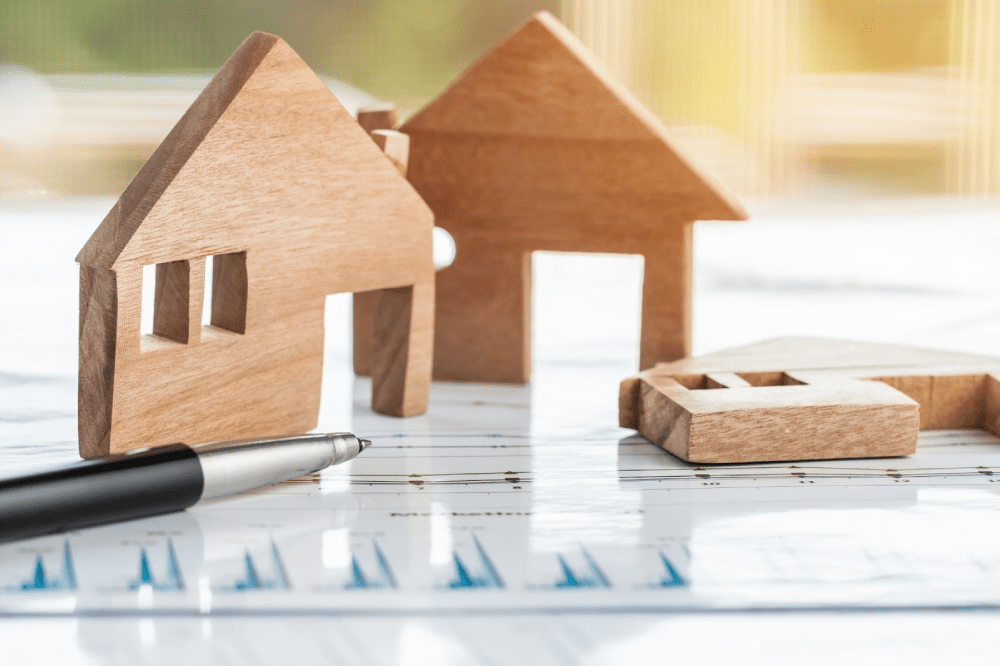

What Are Tariffs and Why Do They Matter for Housing?
Tariffs are taxes governments place on imported goods to protect domestic industries or generate revenue. When the U.S. imposes tariffs on construction materials from other countries, American companies must pay more to import these products. This cost increase doesn’t disappear — it gets passed down through the supply chain until it reaches consumers.
The connection between tariffs and the housing market is clear when considering what goes into building a home. Steel for framing, aluminum for windows and siding, lumber for structural elements, and concrete components often come from international suppliers. When these materials become more expensive due to tariffs, every new home costs more to build.
Trade policy affects housing economics in ways that extend beyond just material costs. Tariffs can trigger retaliation measures from other countries, disrupting established supply chains. Builders who rely on predictable pricing from overseas supply chains suddenly face uncertainty, making it harder to bid on projects accurately.
The ripple effects touch every aspect of the construction industry. Small contractors working on single-family homes feel the impact just as much as large developers building entire neighborhoods. Even renovation projects become more expensive when materials cost more.
How Tariffs Affect Construction Costs
When tariffs increase the price of imported building materials, construction costs rise immediately. Builders can’t absorb these increases indefinitely — they need to maintain profit margins to stay in business. The result is higher prices for new homes and significant pressure on the entire industry.
The 2018 lumber tariffs perfectly illustrate how tariffs affect housing market conditions. When the U.S. imposed tariffs on Canadian lumber, prices jumped dramatically. A typical new home required about $9,000 more in lumber costs, and builders had little choice but to pass these expenses to buyers.
Steel and aluminum tariffs create similar pressures. These materials are essential for everything from structural beams to roofing systems. When tariffs make steel more expensive, that cost shows up in every building project. Homebuilders and developers must adjust their pricing strategies, often leading to sticker shock for potential buyers.
The secondary effect is reduced new housing supply. When building becomes too expensive, some developers postpone or cancel projects entirely. This reduction in new home construction worsens existing inventory shortages, creating additional upward pressure on prices across the market.
Smaller builders often struggle even more because they lack the financial resources to weather cost volatility. This can lead to market consolidation, where only the biggest players survive, potentially reducing competition and innovation in home construction.
How Will Tariffs Affect Housing Prices?
The direct link between construction costs and housing prices means that tariff-related expense increases eventually show up in home values. When materials cost more, builders charge more for new homes. Since housing markets are interconnected, higher prices for new construction also push up values for existing homes.
How tariffs affect housing market pricing varies by region. Urban areas with more high-rise construction using steel and concrete may see different impacts compared to suburban markets relying heavily on wood framing. Rural markets might experience less immediate effects if local materials dominate construction.
Simply put, tariffs increase housing prices, and limited inventory compounds these price pressures. When fewer new homes enter the market due to higher construction costs, buyers compete more intensely for available properties. This competition drives up prices even for homes built before tariffs took effect.
The price effects aren’t always immediate or uniform. Some builders absorb initial cost increases, hoping tariffs are only temporary. Others adjust pricing immediately to protect margins. This creates market volatility that can confuse both buyers and sellers.

Impact on Mortgage Lenders and Borrowers
Rising home prices directly affect mortgage lending by changing the fundamental economics of home purchases. When houses cost more due to tariff-related construction increases, buyers need larger loans to purchase the same properties. This shift affects debt-to-income ratios, potentially disqualifying some borrowers who would have qualified at lower price points.
Lenders must prepare borrowers for pricing volatility that tariffs can create. Unlike gradual price appreciation, tariff-related increases can happen quickly and unpredictably. Borrowers who start shopping in one price range might find themselves priced out within months if material costs spike.
The effect on appraisals also creates additional lending complexity. Appraisers must determine whether recent price increases reflect genuine market conditions or temporary tariff-related distortions. This uncertainty can make it harder for lenders to assess appropriate loan amounts and risk levels.
Larger loan amounts mean higher monthly payments, which affects affordability calculations that determine lending approval. Borrowers might need to adjust their home buying budgets significantly or wait for market conditions to stabilize before making purchases.
The best lenders help borrowers understand these market dynamics rather than simply processing loan applications. Education about mortgage rates and market timing is even more valuable when external factors like trade policy affect housing costs.
Broader Economic Implications
Tariffs and the housing market intersect with broader economic trends that affect everyone, not just home buyers and sellers. When governments impose tariffs, prices rise across virtually every category of consumer goods, from groceries and clothing to electronics and automobiles. This widespread price inflation creates economic pressures that eventually circle back to affect housing markets in unexpected ways.
The inflation ripple effect touches every household budget. Families paying more for food, gas, and everyday necessities have less money available for housing costs. This reduced purchasing power can dampen demand for homes, even as construction costs push prices higher. The result is a complex market dynamic where affordability becomes a bigger challenge from multiple directions.
The Federal Reserve (“The Fed”) responds to tariff-driven inflation by increasing borrowers’ interest rates to slow the overheated economy. When the Fed increases rates to combat rising prices across all sectors, mortgage rates usually follow suit, though the Fed doesn’t directly influence mortgage rates. This creates a double squeeze where home buyers face both higher purchase prices due to construction costs and higher borrowing costs due to monetary policy.
The broader economic effects extend to employment and wages, too. While some domestic industries might benefit from tariff protection, consumers in every sector face higher costs. Workers might then ask for higher wages to maintain their purchasing power, which can fuel additional inflation cycles that affect housing affordability.
Monetary policy adjustments in response to economy-wide inflation can also significantly impact decisions about when to refinance existing mortgages. Homeowners watching their grocery bills and utility costs rise might find refinancing less attractive if rates have increased due to Fed policy responses to tariff-related inflation.
What Home Buyers Should Know About Tariffs and Housing
Smart buyers adjust their strategies to protect their investments and find better deals when tariffs drive up housing costs. Here are a few tips to help you when buying a house during uncertain economic times:

- Expand your search criteria: Look at older homes instead of new construction, consider different neighborhoods, and stay open to properties that might have been overlooked by other buyers during high-cost periods.
- Time your purchase carefully: Monitor trade policy announcements and remember that tariff effects change quickly, unlike normal market cycles. The housing market under Trump has shown how rapidly conditions can shift. As long as you can reasonably afford the house you want, there’s no need to try to time the market.
- Work with experienced professionals: Choose lenders who understand how trade policies affect local markets and builders who can explain their material sourcing strategies during volatile periods.
- Lock in your mortgage rate early: Secure loan terms quickly once you find a property since you can control borrowing costs even when you can’t control material prices.
- Prepare for higher costs across the board: Factor in that renovation materials will also cost more, and consider whether waiting for policy changes makes sense for your timeline.
Final Notes
Understanding how tariffs affect housing market conditions helps you make smarter decisions whether you’re buying your first home or your fifth. Trade policies might seem removed from your daily life, but they directly impact construction costs, home prices, and mortgage rates. Working with a lender who understands these connections can help you adapt your strategy when market conditions change quickly due to policy shifts.
At Griffin Funding, we help borrowers succeed regardless of market volatility. Our experienced team understands how external factors like tariffs influence local housing markets and can guide you toward loan options that work for your situation. The Griffin Gold app can also help you manage your finances and find the right financing option, even when tariffs create uncertainty in housing costs.
Ready to explore your options? Get started online today or reach out to learn more.
Find the best loan for you. Reach out today!
Get StartedRecent Posts
Net Operating Income: Definition, Formula, & Examples
What Is Net Operating Income (NOI)? Net operating income measures how much money your investment property gene...
Best DSCR Lenders: Griffin Funding vs Angel Oak vs Kiavi vs Visio vs Lima One vs Easy Street
What to Look for in a DSCR Lender Choosing the best DSCR lender for your unique situation means evaluating sev...
Cash on Cash Return in Real Estate: Definition, Formula, & Examples
What Is Cash on Cash Return? Cash on cash return (CoC) is a metric that measures the annual income you generat...









